Describe How the Rain Shadow Effect Works
The mass of the rain per second that strikes the roof is 0060 kg every second. The rain shadow effect occurs as warm moist air rises against high elevations of land and drops its water along the way.
A rain shadow is an area of significantly reduced rainfall behind a mountainous region on the side facing away from prevailing winds known as its leeward side.
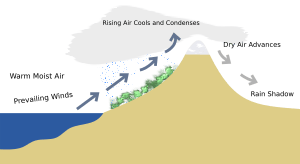
. We call this dry side of the mountain the leeward side. A rain shadow is a patch of land that has been forced to become a desert because mountain ranges blocked all plant-growing rainy weather. Evaporated moisture from water bodies such as oceans and large lakes is carried by the prevailing onshore breezes towards the drier and hotter inland areas.
The air cools as it rises and water vapor can condense to form clouds. His shadow is 6 feet long. On one side of the mountain wet weather systems drop rain and snow.
Describe how the rain shadow effect works. Briefly describe how Doppler works. This creates a region on the far side of the mountain range that is relatively deficient in precipitation to the point of forming a rain-shadow desert.
In a rain shadow its warm and dry. Rain Shadow Effect An area having little precipitation due to the effect of a mountain range which causes the winds to lose their moisture on the windward side and causes the leeward side to be dry. Rain Shadow Effect As a parcel of air rises up the windward side of a mountain range it has its moisture squeezed out.
The rain shadow effect occurs as warm moist air rises against high elevations of land and drops its water along the way. Rain Shadow The. Lake Effect Snow In addition to rain shadows some locations near the Great Lakes and other large bodies of water such as Lake Tahoe experience lake effect snow.
As the cool air descends it warms and expands reducing its possibility of precipitation. Because the air has lost much of its original water content as it descends and warms its relative humidity decreases. How tall is the tree scince During a rain storm rain comes straight down with velocity Vi -15 ms and hits the roof of a car perpendicularly.
ExThe Tibetan Plateau where rain does not make it past the Himalayas leading to an arid climate on the leeward side of the mountain range. The air on the leeward side is dry. This creates a region on the far side of the mountain range that is relatively deficient in precipitation to the point of forming a rain-shadow desert.
Leeward this would be the side of the object that is sheltered or away from the wind. Prevailing winds are the winds that occur most of the time in a particular location on the Earth. Thus when the air begins to descend the leeward side of the mountain it is dry.
On one side of the mountain wet weather systems drop rain and snow. When that water becomes too dense and cool it falls to the ground in. If an air mass is forced to rise for example over a mountain range it expands because of the lower pressure at higher altitudes and this expansion leads to cooling.
It keeps the windward side of mountain ranges lush with lots of vegetation and moisture but the leeward sides are arid deserts. How this plays a role in the formation of deserts is mountain ranges force high moisture content air to travel over the mountains. Orographic Lift Ascending or lifting air caused by rising terrain such as the mountains.
A rain shadow works similarly. What is the rain shadow effect and how does it work. A rain shadow is a patch of land that has been forced to become a desert because mountain ranges blocked all plant-growing rainy weather.
The Rain Shadow Effect. The effect itself Orographic lifting or the rain shadow effect is a fascinating process that occurs naturally. This process causes the rain-shadow effect which is illustrated in the figure below.
The clouds can release the water as pre- cipitation. Its where moist air gets blocked by mountains. Therefore this side of the mountain tends to be wetter with more vegetation.
When winds move over a body of water water will evaporate develop large storm clouds and generate significant snowfall and sometime blizzards. Water that is picked up from a body of water travels through the atmosphere as clouds. On the other side of the mountainthe rain shadow sideall that precipitation is blocked.
The protected side of a mountain range is also called the lee side or the down-wind side. So lets familiarize ourselves with the basic types of clouds. A rain shadow is a dry region of land on the side of a mountain range that is protected from the prevailing winds.
These areas are called rain shadows and are commonly deserts. The rain shadow effect is a reduction of rainfall and loss of moisture from an area of land on the opposite side of a mountain facing away from prevailing surface winds. Air rises to flow over mountains.
On the other side of the mountainthe rain shadow sideall that precipitation is blocked. Rain shadow effect Author. Do an internet search and copy and paste an example of each of the following types of clouds in the chart below.
The air over large bodies of water tends to be dense warm and moist. What is the Rain shadow effect. A rain shadow forms when moist winds head towards a set of mountains and get forced upwards by them.
The rain shadow effect occurs when wind is forced up the slopes of a mountain and drops most of its moisture on the windward side. Assuming that the rain comes to new social studies. This moist air often comes from the sea or from another large body of water.
A rain shadow is a dry area on the side of a mountain opposite to the wind. From this animation of the Rain Shadow Effect you now know why clouds form. If wind is approaching from the west the rain shadow is on the east.
Lamar HS Last. A rain shadow works in the same way.

Rain Shadow Effect What Is A Rain Shadow Video Lesson Transcript Study Com

Rain Shadow Effect What Is A Rain Shadow Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
Comments
Post a Comment